Understanding the Risks of Benzodiazepines
Explore the hidden dangers of commonly prescribed sleep and anxiety medications, and learn how they can impact cognitive health, especially in older adults.
The Hidden Dangers of Prescription Sleep Medications
Protect Your Cognitive Health
Discover the potential risks associated with prolonged use of benzodiazepines and how to safeguard your well-being.
The Perils of Benzodiazepine Overuse
Assessing Potential Risks
Benzodiazepines, including Xanax and Lorazepam, are widely prescribed to alleviate anxiety and aid sleep. However, their misuse can lead to severe consequences, such as dependency and cognitive decline. While effective for short-term relief, long-term use poses significant health risks.
Statistics reveal that over 5 million adults misuse these medications annually, often without realizing the potential for addiction and other adverse effects. The drugs slow down the nervous system, leading to side effects like drowsiness and memory issues, which can escalate with overuse.
Particularly concerning is their impact on older adults, who are the largest consumers of these drugs. The slowing of cognitive functions and increased risk of negative interactions with other medications necessitate caution and awareness.
looking at the data
Benzodiazepine Misuse Statistics
Recent studies have highlighted the concerning trend of benzodiazepine misuse among adults. According to the National Survey on Drug Use and Health, over 30 million adults reported using benzodiazepines in the past year, with more than 5 million individuals admitting to misuse. This misuse is defined as taking the medication in a manner not directed by a healthcare professional.
Adult Usage Statistics for Benzodiazepines
Prevalence of Benzodiazepine Use Among Adults
30.6 million adults use annually
25.3 million reported taking as-prescribed
5.3 Million reported misuse
Adults Misusing Benzodiazepines Statistics
Prevalence of Benzodiazepine misUse Among Adults
%
adults reported misuse (overall)
%
Ages 18-25 (Highest proportion of misuse)
%
Adults 65+ (lowest proportion of misuse)
Benzodiazepines in Popular Culture
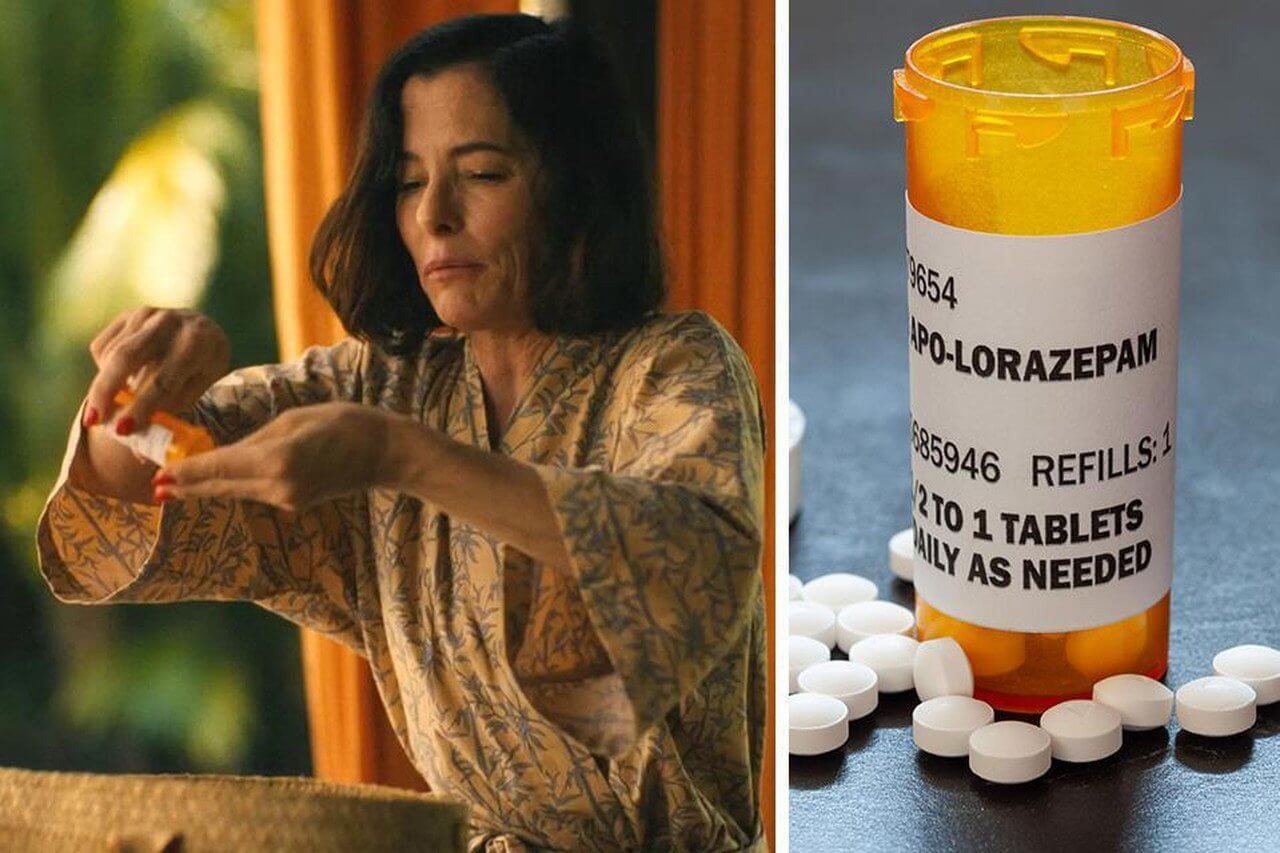
The HBO series White Lotus offers a dramatized glimpse into the casual use of Lorazepam, highlighting the potential for misuse. Parker Posey’s character, Victoria Ratliff, humorously yet alarmingly showcases the ease with which these drugs can be overused, often in combination with alcohol.
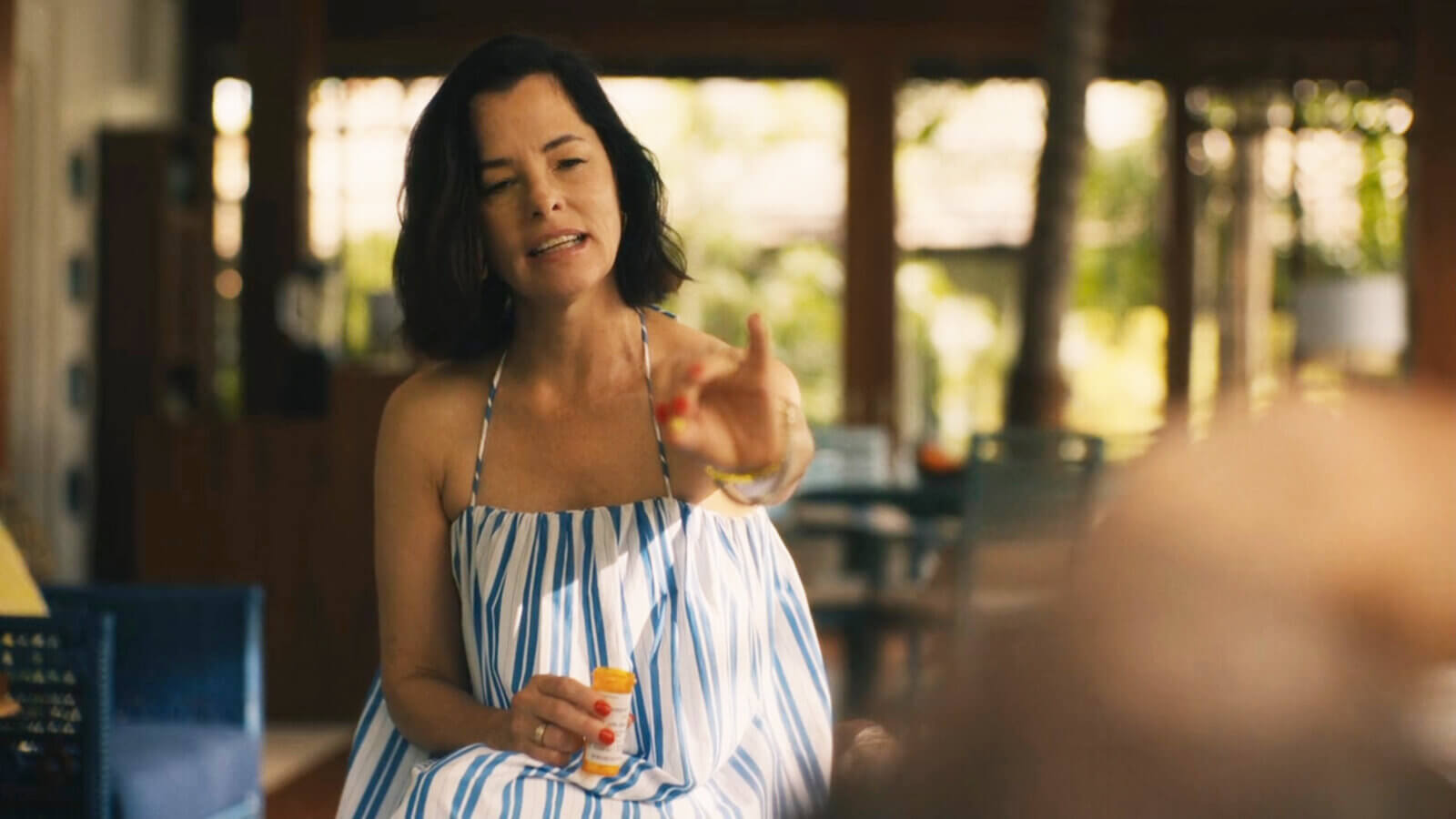

A Cautionary Tale
This portrayal underscores the real-world issues surrounding benzodiazepine use, emphasizing the importance of understanding their effects and the dangers of mixing them with other substances. The show serves as a reminder of the need for responsible medication use.
Lessons from Fiction
White Lotus not only entertains but also educates viewers on the potential pitfalls of prescription drug dependency. It highlights the necessity for medical guidance and the exploration of alternative treatments for anxiety and sleep disorders.

Understanding Benzodiazepines
The Role of Benzodiazepines in Medicine
Benzodiazepines are a class of psychoactive drugs primarily prescribed to manage anxiety disorders, insomnia, and certain seizure disorders. These medications work by enhancing the effect of a neurotransmitter called gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), which helps to calm the nervous system. Commonly known benzodiazepines include Xanax, Ativan, and Klonopin. While effective for short-term relief, they are not intended for long-term use due to the risk of dependence and cognitive side effects.
In clinical settings, benzodiazepines are also used for their muscle relaxant properties and to induce sedation before medical procedures. Despite their therapeutic benefits, these drugs must be prescribed and monitored carefully to prevent misuse and potential addiction. Understanding their pharmacological action is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers to ensure safe and effective use.
Side Effects
Understanding Benzodiazepine Side Effects
Benzodiazepines, including Xanax and Lorazepam, are known for their calming effects, but come with a range of side effects. Common issues include drowsiness, memory lapses, and impaired coordination. When these drugs are overused, the consequences can escalate to severe dependency, cognitive dysfunction, and even life-threatening conditions such as coma or respiratory depression.
common side effects
drowsiness
dizziness
dry mouth
confusion
muscle weakness
light-headedness
unsteadiness
slurred speech
nausea
constipation
memory problems
blurred vision
less common side effects
increased saliva production
tremors (shaking)
headaches
low blood pressure
difficulty urinating
digestive disturbances
sight problem (double vision)
rashes
changes in sexual desire
incontinence (loss of bladder control)
Paradoxical Side Effects
Unexpected Reactions
Benzodiazepines may, at times, elicit responses that counteract their intended soothing effects, commonly referred to as paradoxical reactions.
anxiety
delusions
aggressive behavior
hallucinations
irritability
nightmares
restlessness
personality changes
agitation
depression
inappropriate behaviour
depersonalization
derealisation
psychosis
rages
suicidal thoughts / behaviors
Overuse
Risks of Long-Term Benzodiazepine Use
Overuse of these medications can lead to a dangerous cycle of dependency, where the body becomes reliant on the drug to function normally. This dependency can make withdrawal difficult, with symptoms like anxiety, insomnia, and physical discomfort. It’s vital for users to be aware of these risks and seek professional guidance to manage their medication use safely.

Dependence
Long-term use of benzodiazepines poses significant health risks, particularly the development of physical dependence. Patients who use these medications over extended periods may find themselves requiring higher doses to achieve the same therapeutic effects, a phenomenon known as tolerance. This can lead to a cycle of increasing dosage and heightened risk of addiction.

Withdrawal
Withdrawal symptoms are another concern for those attempting to discontinue benzodiazepine use after prolonged periods. Symptoms such as anxiety, insomnia, and irritability can be severe and may require medical supervision to manage safely. Gradual tapering under the guidance of a healthcare professional is often recommended to minimize withdrawal effects.
Alternative Treatment
Given these potential dangers, it is essential for patients and healthcare providers to weigh the benefits and risks of long-term benzodiazepine therapy carefully. Exploring evidenced-based, non-pharmacological interventions, such as cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) for anxiety management, and cognitive behaviroal therapy for insomnia (CBT-i), can offer effective alternatives for managing anxiety and sleep disorders without the associated risks of medication dependence.
Risks for Older Adults
cognitive decline
concerning use among older adults
Prevalence of Benzodiazepine Use Among Older Adults
%
Overall prevalence amongst adults
%
Ages 50-64 (Highest proportion of use)
%
Adults 65+
drug interaction risks
Medication Interaction Awareness

Understanding the interactions between benzodiazepines and other substances is crucial for safe use. Alcohol, in particular, can significantly amplify the sedative effects of these drugs, leading to increased drowsiness and impaired judgment. This combination can be particularly hazardous, potentially resulting in accidents or severe health complications.
Patients should be informed about the risks of mixing medications and substances. Consulting with healthcare professionals about all medications and supplements being taken can prevent harmful interactions. Being proactive about these discussions ensures safer treatment plans and reduces the risk of adverse effects.
Understanding Withdrawal
The Struggle of Weaning Off Benzodiazepines
Physiological dependence on benzodiazepines often leads to withdrawal symptoms that can include:
- sleep problems
- irritability
- increased anxiety / tension
- panic attacks
- shakiness
- sweating
- difficulty concentrating
- nausea
- some weight loss
- heart palpitations
- headaches
- muscle pain
- stiffness
- perceptual changes


In White Lotus, Victoria Ratliff can’t seem to get through the day without popping Lorezepam like candy, sometimes downing them with white wine at dinner. Her overuse of the pills left her slurring her words, zoning out, and dozing off at the dinner table. At one point in episode 4, Victoria’s daughter Piper exclaims, “You don’t have enough lorazepam to get through one week at a wellness spa?” Yet the show failed to demonstrate any real withdrawal symptoms in the character, other than a casual, “I guess I’ll have to drink myself to sleep” after discovering that her pills had gone missing.


In reality, when someone stops taking benzodiazepines after normal doses, they tend to experience several symptom patterns. The most common is a temporary return of anxiety and insomnia that starts within 1 to 4 days, followed by a more intense withdrawal syndrome that typically lasts 10 to 14 days. Lastly, symptoms of anxiety may return and persist until alternative treatment begins. While dependence can develop after long-term use of therapeutic doses, it remains unclear how many patients will face withdrawal or how long or at what dose increases the risk of dependence. Withdrawal symptoms seem to be more intense after stopping high doses or fast-acting benzodiazepines. Additionally, having a dependence on alcohol or other sedatives might raise the risk of becoming dependent on benzodiazepines, but it’s challenging to definitively compare the abuse potential of different benzodiazepines.
Seeking Professional Guidance
Consulting Experts for Safe Alternatives

When considering the cessation of benzodiazepines, individuals often face a daunting journey marked by withdrawal symptoms. These symptoms can range from mild discomfort to severe physical and psychological effects, including anxiety, insomnia, and even seizures. The process of weaning off these medications requires careful planning and often a gradual reduction in dosage to minimize these adverse effects. It’s crucial to approach this transition with patience and professional guidance to ensure safety and effectiveness.
The Importance of Expert Advice
For those looking to explore alternative treatments for anxiety and sleep disorders, consulting with health care professionals is vital. Experts can provide personalized treatment plans that may include cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), which has been shown to be effective in managing symptoms without the risks associated with medication dependency. By seeking professional advice, individuals can explore a variety of therapeutic options tailored to their specific needs, promoting long-term health and wellness.
Dr. Dixon is expertly trained and experienced to provide cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) for anxiety managment and CBT for insomnia (CBT-i). We invite you to reach out for more information or to schedule an appointment.


















